
read more and converting investments into cash (banks and financial institutions)įinancial institutions Financial Institutions Financial institutions refer to those organizations which provide business services and products related to financial or monetary transactions to their clients.
Maintaining liquidity Liquidity Liquidity is the ease of converting assets or securities into cash. Governing regulations to maintain stability (central banks and governments). Financial Data about individuals like past Months Bank Statement, Tax return receipts helps banks to understand customer’s credit quality, repayment capacity etc. Collecting and distributing financial information Financial Information Financial Information refers to the summarized data of monetary transactions that is helpful to investors in understanding company’s profitability, their assets, and growth prospects. A firm may face this due to incompetent business decisions and practices, eventually leading to bankruptcy. Protecting them against financial risks Financial Risks Financial risk refers to the risk of losing funds and assets with the possibility of not being able to pay off the debt taken from creditors, banks and financial institutions. 
Giving participants a way of earning interest in the form of time value (investment institutions).Providing a way of making payments (banks).Also, it allows participants to benefit by: Consequently, it resulted in a financial system structure capable of efficiently allocating economic resources to stimulate growth. However, it challenges an economy in determining when, where, to whom to distribute its resources.
#Elements financial drivers#
This problem, referred to as scarcity, is one of the significant drivers of an economy. In any functional economy, economic resources are limited, with individuals having unlimited wants and desires. A specific set of rules drafted under different government policies is required for a stable financial system operating at corporate, national, and international levels.
 It serves different purposes in an economy, such as working as payment systems, providing savings options, bringing liquidity to financial markets, and protecting investors from unexpected financial risks. It gives investors the ability to grow their wealth and assets, thus contributing to economic development. A financial system consists of individuals like borrowers and lenders and institutions like banks, stock exchanges, and insurance companies actively involved in the funds and assets transfer. read more, and financial services are the components of the financial system. These are liquid assets because the economic resources or ownership can be converted into a valuable asset such as cash. read more, financial assets Financial Assets Financial assets are investment assets whose value derives from a contractual claim on what they represent. It provides a platform for sellers and buyers to interact and trade at a price determined by market forces. read more, financial markets Financial Markets The term "financial market" refers to the marketplace where activities such as the creation and trading of various financial assets such as bonds, stocks, commodities, currencies, and derivatives take place.
It serves different purposes in an economy, such as working as payment systems, providing savings options, bringing liquidity to financial markets, and protecting investors from unexpected financial risks. It gives investors the ability to grow their wealth and assets, thus contributing to economic development. A financial system consists of individuals like borrowers and lenders and institutions like banks, stock exchanges, and insurance companies actively involved in the funds and assets transfer. read more, and financial services are the components of the financial system. These are liquid assets because the economic resources or ownership can be converted into a valuable asset such as cash. read more, financial assets Financial Assets Financial assets are investment assets whose value derives from a contractual claim on what they represent. It provides a platform for sellers and buyers to interact and trade at a price determined by market forces. read more, financial markets Financial Markets The term "financial market" refers to the marketplace where activities such as the creation and trading of various financial assets such as bonds, stocks, commodities, currencies, and derivatives take place. 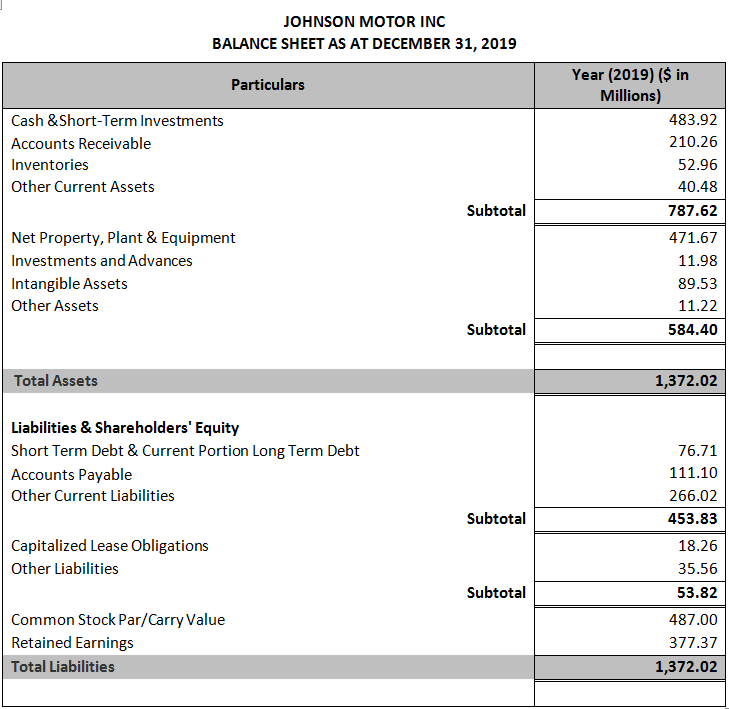

Some of these are banks, NBFCs, investment companies, brokerage firms, insurance companies and trust corporations. Aside from financial institutions Financial Institutions Financial institutions refer to those organizations which provide business services and products related to financial or monetary transactions to their clients. It functions at corporate, national, and international levels and is governed by various rules dictating the eligibility of participants and the use of funds for different purposes. The market participants may include investment banks, stock exchanges, insurance companies, individual investors, and other institutions. Its goal is to efficiently distribute economic resources to promote economic growth and generate a return on investment (ROI) for market participants. A financial system is an economic arrangement wherein financial institutions facilitate the transfer of funds and assets between borrowers, lenders, and investors.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
